Human Saliva samples as the Present of Many Biomarkers
The use of human saliva as a diagnostic instrument for various diseases and conditions has gained more attention due to its non-invasive collection method and ease of access. Saliva is home to numerous biomarkers, including proteins, enzymes, hormones, antibodies, and genetic material, which can be employed to identify and track diseases.
Below are some examples of diseases and conditions for which saliva serves as an effective clinical sample:
1. Oral diseases:
By examining specific bacteria or inflammatory markers, saliva can be employed to detect oral diseases like periodontitis, gingivitis, and dental caries.
2. Viral infections:
Saliva tests can diagnose infections caused by viruses such as HIV, hepatitis B and C, and more recently, SARS-CoV-2, the virus behind COVID-19.
3. Hormonal imbalances:
Saliva can measure hormone levels like cortisol, which can be useful for diagnosing and monitoring conditions such as Cushing’s syndrome or Addison’s disease.
4. Cancer:
Early detection and monitoring of certain cancers, such as oral, pancreatic, and lung cancer, can be aided by salivary biomarkers.
5. Genetic disorders:
Salivary genetic material can be used to diagnose genetic disorders like cystic fibrosis or specific hereditary diseases.
6. Ovulation and fertility:
By detecting changes in hormone levels or specific enzymes indicating ovulation, saliva can be used to monitor a woman’s fertility.
7. Stress and psychological conditions:
Salivary cortisol levels can be employed to evaluate stress and monitor the efficacy of stress-reduction therapies.
8. Drug monitoring and abuse detection:
The presence of drugs or their metabolites can be detected using saliva, making it a valuable tool for drug monitoring and abuse detection.
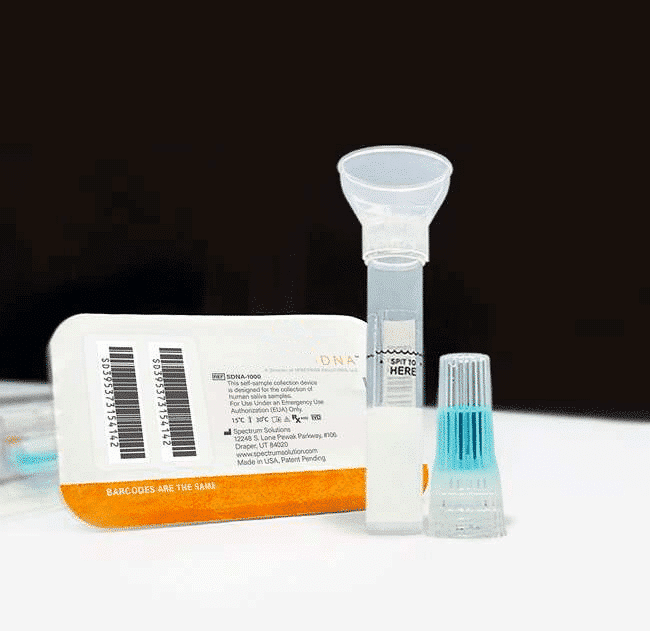
Saliva Collection kit
It is important to acknowledge that saliva testing may not always be the most accurate or suitable diagnostic method for every disease or condition. In certain cases, other diagnostic methods, such as blood tests or imaging, may offer more accurate or comprehensive data. The choice of diagnostic method depends on the disease or condition being tested and the patient’s specific needs.
Collecting saliva samples is generally straightforward and non-invasive. The following steps outline the proper collection and preservation of saliva samples: A) Preparation: Instruct the person to avoid eating, drinking, smoking, or brushing their teeth for at least 30 minutes to an hour before giving a saliva sample to prevent contamination or dilution of the sample. B) Collection: Various methods can be used to collect saliva samples:
1. Passive drool method:
The person pools saliva in their mouth for several minutes and then gently drools into a sterile collection tube or container.
2. Salivate or swab method:
The person places a sterile cotton swab or absorbent pad in their mouth for several minutes, allowing it to soak up saliva. The swab or pad is then placed in a sterile container or pressed against the container’s walls to release the saliva.
3. Collection devices:
Some commercial saliva collection kits use specialized devices or tubes that simplify saliva collection while minimizing the risk of contamination.
4. Storage:
If the saliva sample cannot be analyzed right away, store it at a low temperature to maintain its effectiveness. Generally, saliva samples can be stored at 4°C (39.2°F) for a short period (up to 24 hours) or at -20°C (-4°F) for long-term storage. In some cases, adding a preservative to the sample may be necessary to maintain the stability of specific biomarkers.
5. Transportation:
If samples need to be transported to a laboratory, they should be properly packaged, adhering to any guidelines provided by the lab, and maintained at a low temperature during transportation.
6. Analysis:
Upon reaching the laboratory, saliva samples should be centrifuged to separate any particulate matter and cellular debris from the liquid portion of the saliva, which contains the biomarkers of interest. The supernatant, or liquid portion, can then be analyzed for the presence of specific biomarkers.
